First map of an insect brain completed
The brain is not only the most complex organ of the body but also one of the most complex things we have yet discovered in the universe. Understanding the human brain and how we think is one of the greatest challenges confronting us.
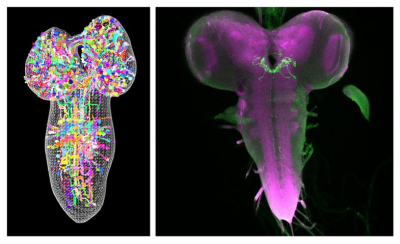
As we continue to study this wonderful organ, we are taking baby steps towards our ultimate goal. An international team of researchers led by Johns Hopkins University and the University of Cambridge recently produced the most detailed diagram of the brain of a larval fruit fly, tracing every neural network in it. The results were published in the journal Science early in March and serves as an archetypal scientific model with brains comparable to humans.
Creating connectomes
The idea of mapping a brain began as early as the 1970s when researchers conducted a 14-year study on roundworms. It resulted in a partial map and also a Nobel Prize. Partial connectomes (map of neural connections in the brain) of several systems, including flies mice, and even humans have since been developed, but these reconstructions usually represent only a tiny fraction of the brain. Comprehensive connectomes have been generated for small species such as roundworms and larval sea squirt.
In this research, the team produced the connectome of a baby fruit fly,’ Drosophila melanogaster larva’. With 3,016 neurons and 5,48,000 connections between them, this is the most expansive map of an entire insect brain ever completed.
Laborious process
Mapping brains is not only difficult, but also extremely time-consuming, despite the latest technology at the disposal of these researchers. To build a complete cellular-level map of the brain, the brain first needs to be sliced into thousands of tissue samples, which are imaged with electron microscopes, before- reconstructing the pieces, neuron by neuron, to create the portrait of the brain.
While the imaging alone took the team nearly a day per neuron (meaning around 3,000 days were spent on the task), the overall work took the University of Cambridge and Johns Hopkins 12 years. The team chose fruit fly larva as the species, for an insect shares a lot of its fundamental biology with humans.
The methods developed by this team for the mapping are applicable to any brain connection project. They are going to make the code used available to whoever attempts to map an even larger animal brain.
Despite the challenges involved, scientists are expected to take on the brain of the mouse, maybe even in the next decade. But as British zoologist and author of ‘The Idea of the Brain’ sums up in his book, knowing where things happen doesn't necessarily translate to knowing how it happens, and our understanding of how still has a long way to go.
Picture Credit : Google













