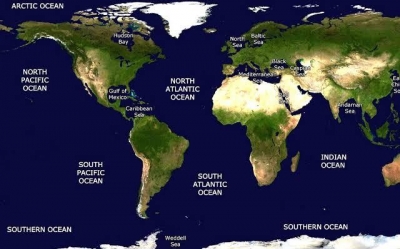
OCEANS
The oceans cover more than two-thirds of the surface of Earth, with an average depth of 3.8 km (2.4 miles), but they are not just huge pools of salt water. The ocean floors are where the great plates of Earth’s crust are splitting apart or grinding together, creating long, high ridges and deep trenches dotted with volcanoes. As a result of this, the oceans are changing their size and shape all the time.
PACIFIC ??EAN
As big as all other oceans put together, the Pacific is shrinking as the edges of its floor slip into deep ocean trenches like the Mariana Trench. The East Pacific Rise, however, is the most active mid-ocean ridge, spreading at up to 22 cm (8.5 in) a year.
ATLANTIC OCEAN
The Atlantic formed when North and South America split from Europe and Africa and gradually moved west. The ocean is still growing as new ocean floor is created at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The ridge breaks the surface in the north to form Iceland, with its volcanoes and geysers.
ARCTIC OCEAN
Most of the Arctic Ocean is covered by thick floating ice in winter. A lot of this melts in spring, allowing sunlight to reach the cold waters and fuel the growth of ocean life. The sea near the North Pole stays frozen in summer, but the area covered by ice is shrinking every year because of global warming.
INDIAN OCEAN
This mainly tropical ocean is notorious for the tsunami that swept across it from Sumatra in 2004. It had a serious impact on nearby coasts and low-lying coral islands like the Maldives, which crown the peaks of an underwater mountain ridge extending south from India.
SOUTHERN OCEAN
With no obvious northern boundaries, the Southern Ocean forms a ring of cold, stormy water around Antarctica. Ice covers a vast area in winter, and the giant icebergs that break off Antarctic glaciers and ice shelves sometimes drift well north.
Picture Credit : Google




