ACIDS AND BASES
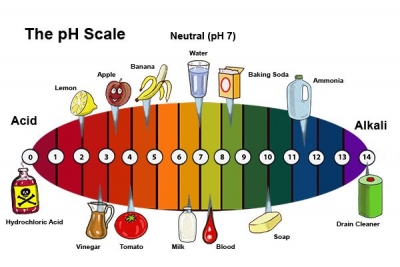
An acid is a substance that produces positively charged particles of hydrogen, called hydrogen ions, when dissolved in water. The more hydrogen ions an acid contains, the stronger the acid is. A base is the chemical opposite of an acid. Bases produce negatively charged particles in water, called hydroxide ions. The more hydroxide ions a base contains, the stronger it is. Bases that dissolve in water are called alkalis.
- INDICATOR PAPER When a strip of indicator paper is dipped into a liquid, the paper changes colour. The colour can be compared to a pH scale to find out the acidity of the solution. pH stands for “potential of hydrogen”, and measures how many hydrogen ions the solution contains.
- CITRIC ACID The sharp taste in citrus fruit such as lemons and grapefruit is due to the citric acid they contain. Citric acid is often artificially added to manufactured foods and drinks to give a tangy sensation that tastes refreshing. Vinegar is made when bacteria convert the ethanol in alcohol into acetic acid.
- VINEGAR The sour taste of vinegar comes from the acetic acid it contains. Every step on the pH scale is 10 times less acidic than the previous step, so acetic acid with a pH of 4 is 1,000 times less acidic than hydrochloric acid.
- HYDROCHLORIC ACID The lower the pH value, the stronger the acid. Hydrochloric acid, created when hydrogen chloride gas dissolves in water, has a pH of about 1. It is highly corrosive, capable of eating through metals.
- CHEMICAL HAZARD Strong acids and bases have to be stored in containers that will not be corroded by the chemical within. These containers are labeled with chemical hazard symbols that show the potential dangers.
- STINGER When a bee stings, it injects a mild acid into a person’s flesh, which causes a stinging sensation. Washing the sting with alkaline soap may relieve the pain by neutralizing the acid.
- LIQUID SOAP Soap is a weak base. It is made by combining a weak acid with a strong base, making it only mildly alkaline with a pH of about 8. An indicator paper dipped into liquid soap turns blue.
- LIMESTONE Calcium carbonate, or limestone, is a type of rock formed from the remains of Dead Sea creatures over millions of years. It is an important base, which is quarried and crushed to make fertilizers, paints, ceramics, and cement.
- WATER Pure water is neither acid nor alkali, but neutral, with a pH of 7. Rainwater is slightly acidic, with a pH of 5 to 6, while seawater is slightly alkaline, with a pH of between 8 and 9.
- CLEANING FLUID The strongest bases have a pH of 14 or more. Alkaline solutions with a high pH are used as cleaning materials as they dissolve fats. Cleaning fluids such as bleach and caustic soda have a pH of around 10.
- HYDRANGEAS The hydrangea shrub produces different coloured flowers depending on the acidity of the soil. On acid soils, it produces blue flowers, on alkaline soils, it produces pink or purple flowers, and on neutral soils, it has creamy white blooms.
Picture Credit : Google




