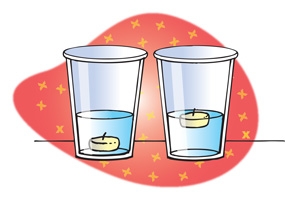
What you need:
Tiny clay balls, a glass and a bottle of soda.
What you do:
Pour the soda into the glass.
Quickly put a small ball of clay into the glass.
What you observe:
The clay ball sinks and then comes up to the surface. This continues for a while.
Why does this happen?
The clay ball sinks because it is heavier than the buoyant force. The buoyant force is the force that keeps a body afloat in water or any liquid. In other words, it is the force exerted by the water to hold up any object. If the weight of the object is greater than the buoyant force, it will sink. If the weight of the object is lesser than the buoyant force, it will float.
The clay ball comes up to the surface because of the bubbles in the soda. Soda is a solution of carbon dioxide in water. When you open a soda bottle, you can see the gas escaping as bubbles. The same thing happens in the glass too. Some of the escaping bubbles collect on the uneven surface of the clay ball. When enough gas has collected, it will actually lift the clay ball to the surface. When the clay ball goes to the surface, carbon dioxide gets released into the air. This makes the clay ball sink. Again when the bubbles collect on the uneven surface of the clay ball, it will rise. The rising and sinking will go on till all the carbon dioxide in the soda gets released into the air. Once this happens, the bubbles will stop forming and the clay ball will not rise.
Repeat the experiment but this time keep the glass partially closed. Find out if the clay ball rises and sinks for a longer time.
Picture Credit : Google



