What is CD-ROM?

CD-ROM’s are important tools for computer users. CD-ROM’s are discs that store words, music, and images. Encyclopedias, games, and other programs that would require greater storage capacity can fit onto one CD-ROM. CD-ROM stands for computer disc read-only memory.
When you put a CD-ROM into your computer’s drive, files are copied from the disc to the computer’s hard drive. These files tell the computer how to access all the information on the CD-ROM.
A DVD (digital video disc) is the same size as a CD-ROM but can store much more information. Unlike a CD or CD-ROM, the DVD is able to record data (information) on both the top and the bottom of the plastic disc. And it can record two layers of data on each side. A DVD player can also play CD-ROM’s.
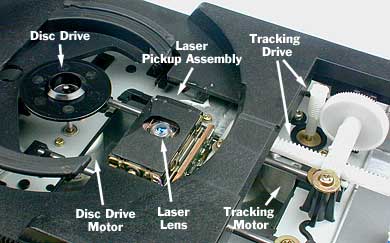
A DVD contains layers of digital data encoded in tiny pits. In a DVD player, a lens focuses a laser beam on the desired layer. As the disc rotates, the pits and the flat areas between them reflect patterns of light to a photo detector, which changes the patterns into electrical signals. A single layer of a DVD has more pits, placed closer together, than an ordinary CD has, and so can store more data.
Picture Credit : Google