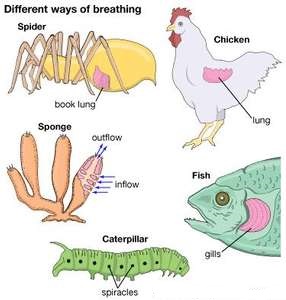
All animals need oxygen to survive. They get it either by breathing air or by absorbing oxygen from water into their body. Dolphins live in water and breathe air through the blowhole on top of their head. All vertebrate animals that live on land have lungs. When we breathe in, the muscle below the rib cage (called the diaphragm) is pulled down, and air gets sucked into the rib cage, filling the lungs. Blood cells circulating through tiny blood vessels near the lungs pick up oxygen and carry it around the body to the sites of respiration. Air is then forced out of the lungs as the diaphragm bows upwards. Birds are different from humans in many ways. As you probably know, they fly, and their bodies are well adapted for flight. Their lungs are very efficient: they take in much more oxygen per breath than other animals do. Because they get this extra oxygen they have lots of energy to direct to the flight muscles in their wings – they can flap away for hours! Frogs and toads have lungs, but when they are in water they can also breathe through their skin.
Picture Credit : Google

