 Soon after the development of the atom bomb in 1945 scientists started developing a more powerful bomb. As a result, they managed to develop another highly destructive bomb called the ‘hydrogen bomb’. The first hydrogen bomb was tested in 1952 by the American scientist Edward Teller and his team. It was a 10 megaton bomb, about 700 times more powerful than the atom bomb dropped in Hiroshima.
Soon after the development of the atom bomb in 1945 scientists started developing a more powerful bomb. As a result, they managed to develop another highly destructive bomb called the ‘hydrogen bomb’. The first hydrogen bomb was tested in 1952 by the American scientist Edward Teller and his team. It was a 10 megaton bomb, about 700 times more powerful than the atom bomb dropped in Hiroshima.
The hydrogen bomb makes use of the phenomenon of ‘nuclear fusion’. In the fusion process, four hydrogen nuclei combine at extremely high temperature to form one helium nucleus. In the fusion reaction tremendous amount of heat energy is liberated. Similar reactions take place in the sun and other stars due to which, they have been producing continuously enormous amounts of heat and light energy.
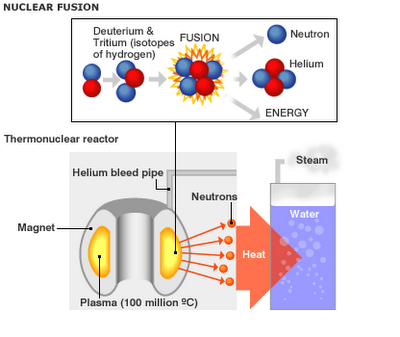
The shell of the hydrogen bomb is made of a strong alloy. Two isotopes of hydrogen (deuterium and tritium) are kept inside this cover. One atom bomb is also enclosed in the same shell to initiate the fusion reaction. When the hydrogen bomb is to be exploded, the atom bomb is made to explode first. It produces a temperature of millions of degrees. At this temperature, deuterium and tritium combine together to form a helium nucleus and produce huge quantity of heat. This reaction is completed in one millionth of a second. In fusion, not only the helium nuclei are formed but neutrons are also produced. These neutrons carry out the fission reaction in uranium by which heat is continuously produced to carry out fusion reaction. That is why this bomb is more powerful. For peaceful uses, they can be modified so that the radio activity produced is minimal.
So far hydrogen bombs have been developed by USA, Russia (former USSR), UK, France and China. Erstwhile USSR tested a hydrogen bomb in 1962 whose power was equivalent to 62 megaton TNT.
