|
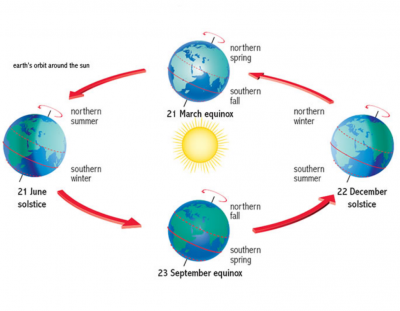
The energy (heat) that the Earth receives from the Sun is a major cause of different weather Conditions. The Sun’s energy in different parts of the Earth depends on where a place is in the world, the time of year and the time of day. |
The energy that the Earth receives from the Sun is the basic cause of our changing weather. Solar heat warms the huge air masses that comprise large and small weather systems. The day-night and summer-winter cycles in the weather have obvious causes and effects.
The effects of currently observed changes in the Sun – small variations in light output, the occurrence of solar particle streams and magnetic fields are very small in the Earth’s lower atmosphere or troposphere where our weather actually occurs. However, at higher altitudes, the atmosphere reacts strongly to changes in solar activity. The ozone layer, at an altitude of 25 kilometers (16 miles), and the ionosphere, which extends upwards in a series of layers above 60 kilometers (37 miles), are produced by solar ultraviolet light and X-rays which ionize the thin air at these altitudes. Although the visible light of the Sun is stable, large variations in X-ray and ultraviolet radiation accompany solar activity, and these variations on the Sun cause major changes in the ionosphere. Some meteorologists believe that the ionospheric changes in turn influence the weather in the lower atmosphere, but the physical mechanism by which this may occur has not been definitely identified. There is much research under way or possible relationships between solar activity and the weather.
Credit: A Meeting with Universe
Picture Credit : Google




