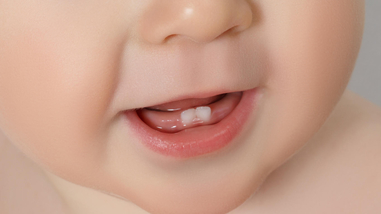
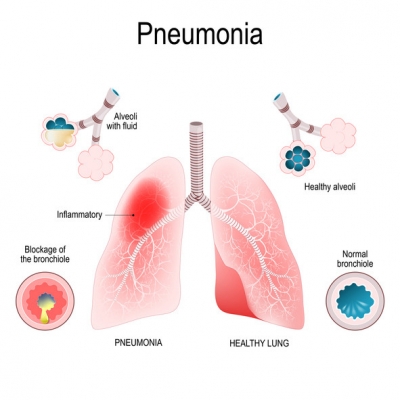
Which is the hardest tissue in the human body is on your teeth?
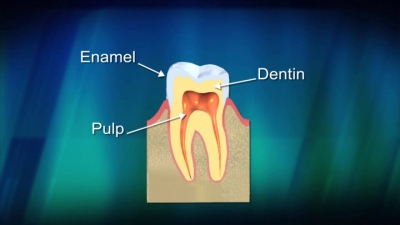
The enamel covering of our teeth also withstands extreme acid-base fluctuations, some of which come from various populations of bacteria that grow in our mouths. Overall, enamel is by far the toughest material in our bodies, and scientists have been examining its structure and composition for decades.
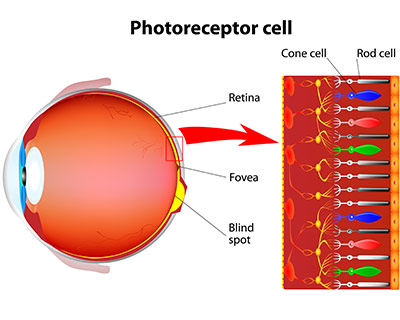
Tooth enamel is clear and only covers and protects the crown (or top part) of teeth. Your dentin makes up the bulk of teeth and is responsible for their color. The roots of teeth are protected by something called cementum. This connective tissue is similar to bone, but not nearly as dense as tooth enamel. If your tooth enamel is weakened because of over-exposure to plaque and acid, supplemental minerals such as calcium and phosphate can strengthen your teeth. Neutralization of acids can help protect your enamel from damage. If your mouth is dry, you may have an issue producing ample saliva, which raises the mouth’s pH and assists in neutralizing acid. Seek the help of your Pella, IA family dentist if upping your hydration with water doesn’t seem to help this issue.
Picture Credit : Google