When do we need fillings?
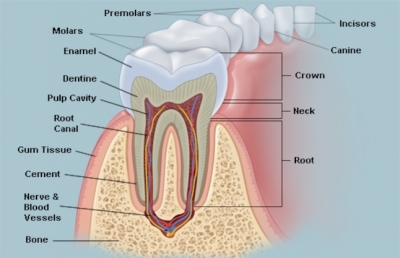
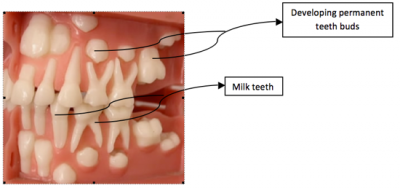
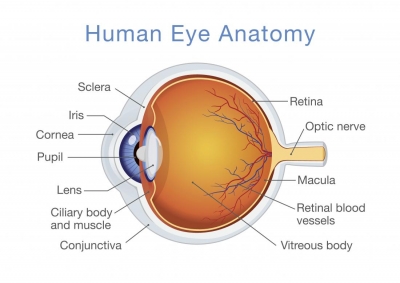
Each tooth has two main parts. The root anchors it firmly in the gum, to withstand the tremendous pressures that are exerted when you bite and chew hard foods like nuts. The crown is the visible part above the gum. It is covered with whitish enamel, which is the hardest substance in the entire body. Under the enamel is a layer of dentine, which is not quite so hard, and absorbs shocks and knocks. In the middle of the tooth are blood vessels, providing nourishment to the tooth’s parts and layers, and nerves, to detect pressure and pain.
Regular visits to the dentist are important for healthy teeth. If you don’t look after your teeth, they may go bad and decay. That means that they may have to be filled or even taken out by the dentist.
Fact File: Germs live in the holes of bad teeth. They eat the good part, which makes the holes deeper. Dentists have to drill out this germy part. The hard outside of teeth cannot grow back. Dentists have to fill the holes with metal to keep the germs out. |
Picture Credit : Google