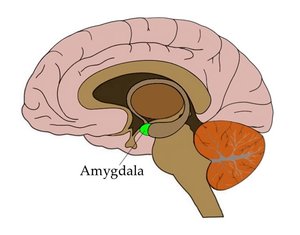
The amygdaloid body is also known as the amygdaloid nucleus. This is an oval structure located within the temporal lobe of the human brain. The structure is a small part of the brain and is closely associated with the hypothalamus, cingulated gyrus, and hippocampus.
The amygdala is an important part of the brain, which assists in responses of fear and pleasure. The abnormal working of the amygdaloid body can lead to various clinical conditions including developmental delay, depression, anxiety, and autism.
A simple view of the information processing through the amygdala follows as- the amygdala sends projections to the hypothalamus, the dorsomedial thalamus, the thalamic reticular nucleus, the nuclei of the trigeminal nerve and the facial nerve, the ventral tegmental area, the locus coeruleus, and the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus. The basolateral amygdala projects to the nucleus accumbens, including the medial shell.
The amygdala is also involved in the modulation of memory consolidation. Following any learning event, the long-term memory for the event is not formed instantaneously. Rather, information regarding the event is slowly assimilated into long-term (potentially lifelong) storage over time, possibly via long-term potentiation. Recent studies suggest that the amygdala regulates memory consolidation in other brain regions. Also, fear conditioning, a type of memory that is impaired following amygdala damage, is mediated in part by long-term potentiation.
Picture Credit : Google

