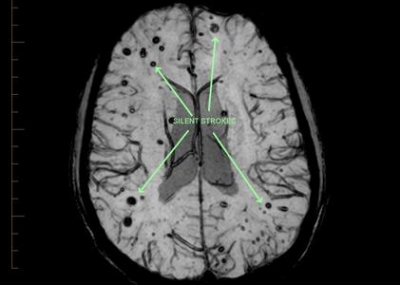
Similar to ischemic brain strokes, silent strokes occur when a portion of your brain suddenly stops receiving blood. It stops oxygen supply to the brain, causing considerable damage to the brain cells. However, a silent stroke is hard to understand because it breaks the blood supply to that part of your brain that has nothing to do with any of your visible functions, such as with ambulation, seeing, or speaking. Therefore, it goes unnoticed.
So, what about Silent Stroke Diagnosis? In most cases, people get to find out about their stroke only when they undergo a CT scan or an MRI of the brain for any other health condition. That is when a doctor can identify that a small portion(s) of your brain has sustained some amount of damage.
Also, if a person has had several episodes of silent stroke, they may notice the onset of several neurological symptoms, including difficulty concentrating and loss of memory.
As per the American Stroke Association, silent or asymptomatic stroke puts you at the risk of having symptomatic brain strokes later on in your life. Recent studies confirm that if you have had multiple episodes of silent strokes, you are at a higher risk for vascular dementia (multi-infarct dementia). The symptoms include:
? Problems with remembering things or loss of memory.
? Losing control over bladder and bowel movements.
? Difficulty in decision-making.
? Emotional outbursts like crying or laughing inappropriately.
? Not identifying previously visited places.
Credit : Quora
Picture Credit : Google




