One of the first things that you should pay attention to when you write is this: See that your verb agrees with the subject you have chosen to write about.
What you want to write about your choice. You can choose Sachin Tendulkar as your topic.
You can choose to write about your neighbours pesky dog that barks all night.
Once you have made your choice about the subject the not thing is to place a verb that matches the subject in the sentences you make.
You know that verbs change.
[1] The verb changes when the action described happened in the past. He wrote the novel several years ago.
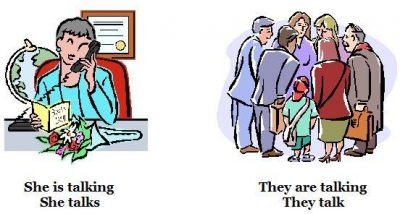
[2] The verb you pick depends on whether the subject is singular (he she, it) or plural (they, you). Of course the pronoun is special and takes the verb an in the present tense.
If your action state of being is in the present tense, you need to write He writes, she writes, it writes. I write you write, we write. They write. He is, she is, it is. I am. You are, we are, they are.
What about “has and “have”? Has” is used for subjects in the singular, when the action/state of being is in the present tense. He has, she has, it has
“Have” is used for subjects in the plural when the action/state of being is in the present tense.
I have, you have, we have, they have
For action verbs, the past tense does not make a difference. It changes to the past tense and remains the same for all subjects.
She/he/It//We//You/They wrote many letters to the government
Read these examples for seeing the rules clearly.
He has done his work. She has done her work. It has done its work.
I have done my work. We have done our work, You have done your work. They have done their work.
“Has” and “have” are also used to show possession. Shenji (He) has a large house. I have a library at home.
As the examples above show, the rules for using “has”, “have” for showing possession are the same as the rules for using them as helping verbs.
Here are some tips to remember
* Singular subjects take on singular verbs. (he/ she/it = is/was/has) * Plural subjects take on plural verbs (you/ we/they = are/were/ have)
* For all the subjects, all the past tense verbs are the same
So, when you write your sentences, watch out! See that the verb agrees with the subject
Pick your verb, place the questions what or “who” before it. The answer is the subject.
Example 1: She has done her work very well. Which is the verb? “has done.”
Who has done? “She”. So “she is the subject. The sentence is “She has done”.
So the verb “has done agrees with the subject “she.” Example 2: Her anms across her chest she lays.
Which is the verb? “lays. Who lays? “She”. So “she” is the subject. So the verb “lays” agrees with the subject “She”.
Picture Credit : Google



