Inside the reproductive system
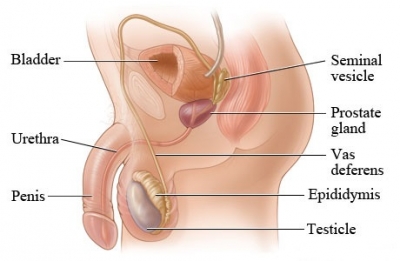
The testes and penis, which are outside the body, are connected by a series of internal tubes and glands. The whole male reproductive system is adapted to produce, mature, and transport sperm to where they can fertilize a female egg.
Sperm factory
Inside the testes, sperm cells are constantly being made. They form inside coiled tubes called seminiferous tubules, before moving to the epididymis where they mature. From there, they can move into the vas deferens, ready to leave the body.
Vas deferens
The vas deferens is a long, muscular tube that travels from the epididymis into the pelvic cavity, to just behind the bladder. Sperm from each testis pass through this tube towards the penis.
Prostate gland
The prostate gland is a walnut-sized structure that is located below the urinary bladder in front of the rectum. The prostate gland contributes additional fluid to the ejaculate. The prostate gland adds substances that protect and nourish the sperm cells.
Erectile tissue
This fills with blood to make the penis stiff enough to enter the woman’s vagina to deliver sperm.
Seminal vesicle
The seminal vesicles are sac-like pouches that attach to the vas deferens near the base of the bladder. This releases fluid that combines with sperm cells to make semen.
Urethra
The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside of the body. In males, it has the additional function of expelling (ejaculating) semen when the man reaches orgasm. Sperm-carrying semen leaves the body through this tube.
Penis
The penis is the male organ for sexual intercourse. It has three parts: the root, which attaches to the wall of the abdomen; the body, or shaft; and the glans, which is the cone-shaped end of the penis. The penis transfers sperm into woman’s vagina.
Testis
The testes are oval organs about the size of very large olives that lie in the scrotum, secured at either end by a structure called the spermatic cord. Also called testicles, the two testes make and release sperm cells.
Scrotum
The scrotum is the loose pouch-like sac of skin that hangs behind the penis. It contains the testicles (also called testes), as well as many nerves and blood vessels. The testes are supported and protected by this pouch or skin and muscle.
Sperm cells
Sperm cells are among the tiniest human cells but the nucleus carries half the genetic instructions for creating a new life. Sperm are well adapted to produce enough energy for the long swim to the female egg.
Picture Credit : Google

