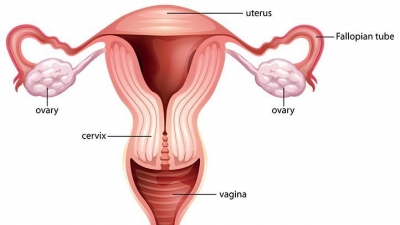
Inside the reproductive system
The uterus is in the middle of the lower abdomen, between the bladder and the rectum. The two ovaries are on either side of the uterus, connected to it by the fallopian tubes.
Inside the ovary
The ovaries contain many thousands of immature eggs, each enclosed in a bag-like follicle. Every month, hormones trigger a process where one of the eggs starts to outgrow the others. When it is mature, the egg is released from the ovary.
Right ovary
The ovary is a ductless reproductive gland in which the female reproductive cells are produced. Females have a pair of ovaries, held by a membrane beside the uterus on each side of the lower abdomen. The ovaries store, then release eggs.
Right fallopian tube
The uterine tubes, also known as oviducts or fallopian tubes, are the female structures that transport the ova from the ovary to the uterus each month. Each fallopian tube connects an ovary with the uterus.
Uterus
This hollow, stretchy organ is where the embryo develops. It functions to nourish and house a fertilized egg until the fetus, or offspring, is ready to be delivered.
Cervix
The cervix is the lower portion of the uterus, an organ of the female reproductive tract. The cervix is the point where the uterus opens into the vagina. Anatomically and histologically, the cervix is distinct from the uterus, and hence we consider it as a separate anatomical structure.
Bladder
This stretchy bag stores and releases urine. The bladder is a pyramidal shaped organ, which sits in our pelvis (the bony structure which helps form our hips).
The main function of the bladder is to store urine, and under the appropriate signals, release it into a tube which carries the urine out of the body.
Rectum
The lowest part of the large intestine is where faeces are stored. The rectum begins at the height of S2-S3 and ends at the perineum. It is about 12 to 16 cm long.
Vagina
The vagina is a fibromuscular (made up of fibrous and muscular tissue) canal leading from the outside of the body to the cervix of the uterus or womb. It is also referred to as the birth canal in the context of pregnancy. The uterus is linked to the outside of the body by this stretchy tube.
Pelvic floor
The uterus and bladder are supported by these strong muscles. These muscles extend across the pelvic region, below other muscles that give humans the ability to walk upright.
Picture Credit : Google

