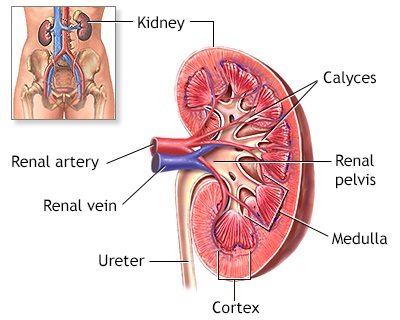
Each kidney has three layers – the outer layer (cortex), inner part (medulla), and central pelvis. Blood flows into the cortex for filtering. The medulla absorbs substances to return to the bloodstream. Waste is taken by tubes to the central pelvis, a collecting area where urine is emptied out into two tubes called ureters, and then passes to the bladder.
Multi-purpose organs
The two kidneys sit high in the back the abdomen. Each one is about the size of a fist, shaped like a bean, and surrounded by a protective layer of tissue.
Adrenal gland
The adrenal glands are small glands located on top of each kidney. They produce hormones that you can’t live without, including sex hormones and cortisol. Cortisol helps you respond to stress and has many other important functions. Adrenaline released from this gland makes the heart beat faster in scary situations.
Renal artery
The renal arteries are responsible for carrying oxygen-rich blood to your kidneys, which in turn help the kidneys rid your body of waste and excess fluid. This artery carries blood into the kidney to be filtered.
Renal vein
The renal vein is an asymmetrically paired vessel that carries the deoxygenated blood from the kidney to the inferior vena cava. Cleaned blood is carried from the kidney by the renal vein.
Outer casing
The kidneys and adrenal glands are wrapped in a layer of fat and strong outer tissue. The outermost layer is a tough connective tissue layer called the renal fascia.
Central pelvis
Urine collects here, and is then sent to the bladder. The pelvis, which is shaped somewhat like a funnel that is curved to one side, is almost completely enclosed in the deep indentation on the concave side of the kidney, the sinus.
Renal cortex
The cortex is the outer part of the kidney. It contains the glomerulus and convoluted tubules.
The renal cortex is surrounded on its outer edges by the renal capsule, a layer of fatty tissue. Together, the renal cortex and capsule house and protect the inner structures of the kidney.
Renal medulla
This layer of the kidney absorbs water, making urine more concentrated. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which then splits up to form the interlobar arteries.
Left ureter
This is one of two tubes that carry urine down to the bladder. There are two ureters, one attached to each kidney. The upper half of the ureter is located in the abdomen and the lower half is located in the pelvic area.
Nephrons
The kidneys contain tiny blood-filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron contains a glomerulus, a bundle of blood vessels surrounded by a capsule. As blood passes through the glomerulus, waste and excess water ooze into the capsule and are carried away by a tubule (tiny tube). Any useful substances, such as glucose, are absorbed by capillaries, while the waste is carried away to form urine.
Picture Credit : Google

