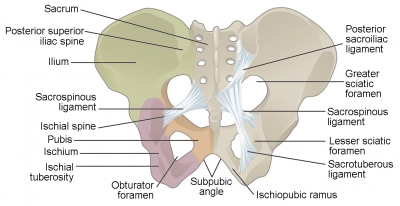
Pelvic girdle
The pelvis is made up of two hip bones, one on each side. Each hip bone has three parts – the ilium, ischium, and pubis. They connect to the sacrum – the lower part of the spine – to form a ring like shape, called the pelvic girdle.
Spine
The spine, or backbone is a column of bones that runs from the pelvis to the neck. The spine is classified into 4 distinct areas.
The cervical area consists of 7 bony parts in the neck. The thoracic spine consists of 12 bony parts in the back area. The lumbar spine consists of 5 bony segments in the lower back area; 5 sacral* bones; and 4 coccygeal* bones (the number of coccygeal bones can vary from 3 to 5). (* By adulthood, the 5 sacral vertebrae fuse to form 1 bone, and the 4 coccygeal vertebrae fuse to form 1 bone.)
Sacrum
At the base of the spine, this triangular-shaped bone connects the two hip bones. It consists of the last four or five vertebrae that by adulthood, fuse together to form a single bone. Located just above the coccyx and wedged between the right and left iliac bones (hip bones), the sacrum forms the back wall of the pelvis. The coccyx, commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the very bottom segment of the vertebral column. The right and left iliac bones are joined together in the front by the symphysis pubis.
Ilium
The largest bone in the pelvis is the ilium, or hip bone. One on each side connects the muscles used to stand and walk. The body of the ilium forms the superior part of the acetabulum (acetabular roof). Immediately above the acetabulum, the ilium expands to form the wing (or ala).
Fixed joint
These bones are held firmly together by strong ligaments. The relatively fixed joint between the sacrum and the lumbar spine is ideal for bearing the load of the upper body. At the most ventral area of the pelvis, there is a fibrocartilaginous joint in the pubic symphysis.
Pelvic cavity
The pelvic cavity is formed by three bilateral pairs of bones (pubis, ilium and ischium) and two posteriorly located bones (sacrum and coccyx). The intestines and bladder are contained here, surrounded by the protective pelvis.
Pubis
The pubis is one of the two smallest bones in the pelvis. In vertebrates, the pubic bone is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three main bones making up the pelvis. The left and right pubic bones are each made up of three sections, a superior ramus, inferior ramus, and a body.
Pubic symphysis
This strong cartilage joint connects the two pubis bones together. It is located in front of and below the urinary bladder. In males, the suspensory ligament of the penis attaches to the pubic symphysis.
Coccyx
Below the sacrum is the Coccyx, or tailbone all that remains of the tail of our distant ancestors. Although the tailbone is considered vestigial (or no longer necessary) in the human body, it does have some function in the pelvis. For instance, the coccyx is one part of a three-part support for a person in the seated position. Weight is distributed between the bottom portions of the two hip bones (or ischium) and the tailbone, providing balance and stability when a person is seated.
Hip joint
The ball shaped top of the thighbone sits in this hollow creating the ball and socket hip joint. The adult os coxae, or hip bone, is formed by the fusion of the ilium, the ischium, and the pubis, which occurs by the end of the teenage years. The 2 hip bones form the bony pelvis, along with the sacrum and the coccyx, and are united anteriorly by the pubic symphysis.
Ischium
The lowest bone in the pelvis the ischium carries all the weight when the body is sitting down. Situated below the ilium and behind the pubis, it is one of these three bones whose fusion creates the hip. The superior portion of this bone forms approximately one third of the acetabulum.
Holes
Small holes in the bones are for nerves and blood vessels.
Picture Credit : Google

