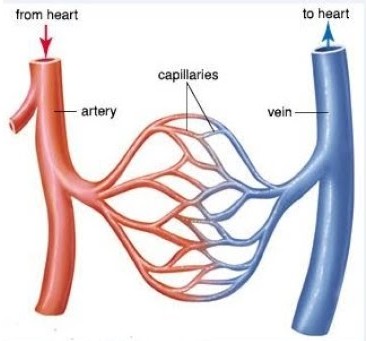
An artery is a vessel that carries blood away from the heart and toward other tissues and organs. Arteries are part of the circulatory system, which delivers oxygen and nutrients to every cell in the body.
Arterial pressure varies between the peak pressure during heart contraction, called the systolic pressure, and the minimum or diastolic pressure between contractions, when the heart expands and refills. This pressure variation within the artery produces the observable pulse that reflects heart activity. The pressure in the arterial system decreases steadily, highest in the aorta and lowest in the venous system, as blood approaches the heart after delivery of oxygen to tissues in the systemic circulation.
Arteries of the systemic circulation can be subdivided into muscular or elastic types according to the relative compositions of elastic and muscle tissue in their tunica media. Larger arteries are typically elastic and smaller arteries are more likely to be muscular. These arteries deliver blood to the arterioles, which in turn deliver blood to the capillary networks associated with the body’s tissues.
Picture Credit : Google




