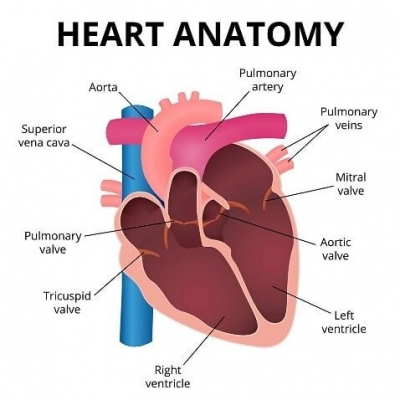
The heart consists of four chambers, two atria (upper chambers) and two ventricles (lower chambers). There is a valve through which blood passes before leaving each chamber of the heart. The valves prevent the backward flow of blood. These valves are actual flaps that are located on each end of the two ventricles (lower chambers of the heart). They act as one-way inlets of blood on one side of a ventricle and one-way outlets of blood on the other side of a ventricle. Normal valves have three flaps, except the mitral valve, which has two flaps.
As the heart muscle contracts and relaxes, the valves open and shut, letting blood flow into the ventricles and atria at alternate times. The following is a step-by-step illustration of how the valves function normally in the left ventricle:
After the left ventricle contracts, the aortic valve closes and the mitral valve opens, to allow blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle.
As the left atrium contracts, more blood flows into the left ventricle.
When the left ventricle contracts, the mitral valve closes and the aortic valve opens, so blood flows into the aorta.
Picture Credit : Google




