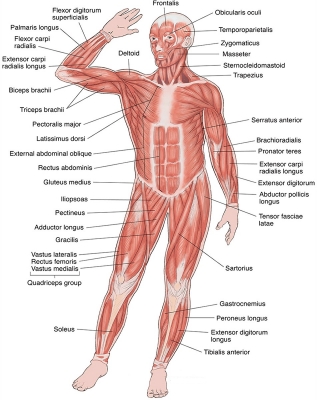
Superficial muscles are just beneath the skin. Those at the front of the body create different facial expressions, move the head forwards and sideways, bend the arms and move them forwards, bend the body forwards and sideways, bend the legs, straighten the knees, and lift the feet.
Frontails
The frontalis muscle is a thin, wide, four-sided muscle located at the top front of the skull (in the area of the forehead). Specifically, this muscle originates from the galea aponeurotica and extends down the forehead and inserts or attaches to the skin around the eyebrows and top of the nose.
Orbicularis oculi
Orbicularis oculi is a paired facial muscle that surrounds each orbit and the adjacent periorbital region. Together with corrugator supercilii and levator palpebrae superioris, it belongs to the circumorbital and palpebral group of muscles that surround the eye. This closes the eye.
Temporalis
The temporalis muscle is a thin, fan-shaped muscle situated within the temporal fossa of the skull. Along with the medial pterygoid, lateral pterygoid and masseter muscles, it belongs to the group masticatory muscles. The temporalis muscle runs superficially, from the temporal bone to the coronoid process of mandible. This muscle pulls the lower jaw up.
Orbicularis oris
Orbicularis oris is a complex circular muscle that surrounds the orifice of the mouth and forms the majority of the lips. It belongs to a large group of muscles of facial expression called the buccolabial group. This muscle purses the lips.
Platysma
This broad sheet of thin muscle lies just under the skin of the neck. It arises in the upper thoracic and shoulder regions from a fascia that covers the pectoralis major and deltoid muscles.
Pectoralis major
The pectoralis major is a paired, superficial muscle located on the anterior surface of the thoracic cage. If you’re a gym lover, you’ll hear these muscles also being referred to as the pecs muscles.
Deltoid
The deltoid is a thick, triangular shoulder muscle. It gets its name because of its similar shape to the Greek letter ‘delta’ (?). The muscle has a wide origin spanning the clavicle, acromion and spine of scapula. It passes inferiorly surrounding the glenohumeral joint on all sides and inserts onto the humerus.
Biceps brachii
The biceps brachii muscle is one of the chief muscles of the arm. The origin at the scapula and the insertion into the radius of the biceps brachii means it can act on both the shoulder joint and the elbow joint, which is why this muscle participates in a few movements of the arm. This bends the elbow.
Rectus abdominis
Rectus abdominis, informally known as the abs muscle, is a long muscle of the anterior abdominal wall. In those with low body fat, it is clearly visible beneath the skin forming the ‘six pack’. It extends from the rib cage all the way to the pubic bone. This paired muscle is often shortened to the “abs”.
Linea alba
This connective tissue connects abdominal muscles on the left and right. It extends between the inferior limit of the sternum and the pubis, separating the rectus abdominis muscles. In leaner, more muscular individuals, it is visible externally as a longitudinal, shallow groove.
Brachioradialis
Brachioradialis is a fusiform muscle located in the lateral part of the posterior forearm. Along with extensor carpi radialis brevis and extensor carpi radialis longus, it comprises the radial group of forearm muscles, which belong to the superficial layer of posterior forearm muscles. This muscle helps to bend the elbow.
External oblique
External abdominal oblique is a paired muscle located on the lateral sides of the abdominal wall. Along with internal abdominal oblique and transversus abdominis, it comprises the lateral abdominal muscles. In a broader picture, these muscles make up the anterolateral abdominal wall together with two anterior abdominal muscles; the rectus abdominis and pyramidalis. This muscle helps to twist the torso.
Tensor fasciae latae
Tensor fasciae latae is a fusiform muscle located in the lateral aspect of the thigh. It belongs to the muscles of the gluteal region, along with the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius and gluteus minimus muscles. This muscle lifts the thigh away from the body.
Pectineus
Pectineus is a flat muscle found in the superomedial part of the anterior thigh. Fascial compartments of the thigh muscles are specific in that each of them is innervated by a particular nerve.
Adductor longus
The adductor longus is a large, fan-shaped muscle located in the medial aspect of the thigh. It belongs to the adductors of the thigh, together with adductor brevis, adductor magnus, adductor brevis, pectineus and gracilis muscles.
Rectus femoris
The quadriceps femoris muscle, commonly known as the quad muscle, is the strongest muscle of the human body. It is located in the anterior compartment of the thigh, together with the sartorius. This is one of the four quadriceps muscles.
Sartorius
This is the longest muscle in the body. Together with the quadriceps femoris, it belongs to the anterior (extensor) muscles of the thigh. It enables you to sit cross-legged.
Vastus medialis
This is one of the four quadriceps muscles. It is the most medial, or inner, of the quadriceps muscles. It extends the entire length of the thigh. The portion of the muscle that is just above the knee is sometimes referred to as the vastus medialis obliquus, or VMO. This muscle is used to extend the leg at the knee and to stabilize the patella, which is also known as the kneecap.
Vastus lateralis
This is one of the four quadriceps muscles, which straighten the knee. Together, the quadriceps acts on the knee and hip to promote movement as well as strength and stability. They provide power for and absorb the impact of daily activities such as walking, running, and jumping.
Gastrocnemius
Gastrocnemius is a large muscle located in the posterior leg. Posteriorly, is the most superficial of the muscles of the leg, and forms the bulk of the calf. This is the largest calf muscle.
Tibialis anterior
Tibialis anterior is a fusiform muscle found in the anterior part of the leg. Lying superficially in the leg, this muscle is easily palpable lateral to the anterior border of tibia. This raises the foot upwards.
Picture Credit : Google

